Weight Loss Surgery Options - Everything
you need to know

Surgical Weight Loss Options
LAP-BANDŽ
System Adjustable Gastric Band
REALIZE?
Adjustable Gastric Band
Roux-en-Y
Gastric Bypass
Duodenal
Switch

What is Bariatric Surgery?
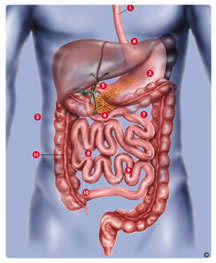 Bariatric
surgery is a surgical procedure performed for
treatment of morbid obesity. The word "bariatric"
comes from the Greek: Baros which means
weight and Iatreia which means medical
treatment. Bariatric surgery has existed since the
1960's, having gone through significant evolution
from the early days of the jejunoileal or
jejunocolic bypass operations and the horizontal
gastroplasty or original "stomach stapling." Other
procedures that are no longer performed include
the silastic ring vertical gastroplasty and the
vertical banded gastroplasty. Modern day
procedures are usually performed by skilled
laparoscopic surgeons and include the Vertical
Sleeve Gastrectomy, the LAP-BANDŽ or REALIZE?
Adjustable Gastric Band procedures, the transected
Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass, and the Duodenal Switch.
Bariatric
surgery is a surgical procedure performed for
treatment of morbid obesity. The word "bariatric"
comes from the Greek: Baros which means
weight and Iatreia which means medical
treatment. Bariatric surgery has existed since the
1960's, having gone through significant evolution
from the early days of the jejunoileal or
jejunocolic bypass operations and the horizontal
gastroplasty or original "stomach stapling." Other
procedures that are no longer performed include
the silastic ring vertical gastroplasty and the
vertical banded gastroplasty. Modern day
procedures are usually performed by skilled
laparoscopic surgeons and include the Vertical
Sleeve Gastrectomy, the LAP-BANDŽ or REALIZE?
Adjustable Gastric Band procedures, the transected
Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass, and the Duodenal Switch.
All the procedures significantly reduce stomach
size. This is accompanied by an altered
physiological and psychological response to
food. The Vertical Sleeve Gastrectomy, the
LAP-BANDŽ or REALIZE? Adjustable Gastric Band
procedures, and the Roux-en-Y Gastric
Bypass reduce the size of the stomach well over
90%. The Duodenal Switch also reduces the stomach
size but not as much. The Duodenal Switch
procedure also and mainly decreases the body's
ability to absorb fat calories and nutrients to
aid in successful weight loss. None of the
surgeries affect the absorption of carbohydrates.
The normal stomach can stretch sometimes over
1000ml. The stomach pouch in these operations is
usually formed from the part of the stomach which
is least susceptible to stretching. When the
patient ingests a small amount of food, mainly
solid protein, the patient feels a sensation of
fullness. The patient learns quickly that
subsequent bites of food must be eaten slowly and
carefully to avoid increasing discomfort and
sometimes vomiting. In the Duodenal Switch, meals
high in fat calories cause significant, oily,
frequent diarrhea and discomfort.
Remember, bariatric surgery is only a tool. The
patient must eat the right foods with vitamins and
supplements to feel full enough in order to avoid
eating carbohydrates and excessive fatty foods to
lose their excess weight in a healthy, nutritional
manner with close follow-up. Exercise, drinking
plenty of liquids and support from Dr. Feng, his
multidisciplinary bariatric team, and other
patients alike are critical in this process.
Eating the wrong foods, not taking the recommended
vitamins and minerals, not exercising can lead to
multiple problems that can result in an unhealthy,
malnourished individual who is still obese.
Dr. Feng specializes in minimally invasive,
advanced laparoscopic bariatric surgery (weight
loss surgery) with expertise in minimally invasive
robotic surgery to optimize surgical precision and
3D visualization. Dr. Feng is dedicated to
patient care. With his comprehensive surgery and
multispecialty programs, he and his team are here
to make you feel comfortable.

Surgical Weight Loss Options

Restrictive Operations
Restrictive operations mainly limit the amount of
food intake and do not interfere with normal
digestive or nutrient absorption process

Vertical Sleeve Gastrectomy / Sleeve Gastrectomy
This restrictive option has an expected Weight
loss of 60-80% of excess body weight
Description of the Vertical Sleeve Gastrectomy
or Sleeve Gastrectomy
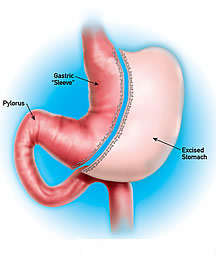 Most
common weight loss surgery performed in the U.S.
Most
common weight loss surgery performed in the U.S.
This is the most modern weight loss procedure
that induces weight loss by restricting food
intake, invented back in 1999 but modified and
refined by Dr. Feng in 2002 to an optimal smaller
size to become a well-established, most popular,
stand-alone procedure.
The Vertical Sleeve Gastrectomy (VSG) is also
commonly known as the Sleeve
Gastrectomy, Restrictive Vertical Gastroplasty, or
just Vertical Gastrectomy (VG). The Vertical
Sleeve Gastrectomy is essentially a newer, better
version of the vertical banded gastroplasty, a
procedure that has been abandoned by virtually all
weight loss surgeons, due to high failure rates
and complications. Dr. Feng surgically reduces
the stomach in size to a long narrow, tube like,
vertical pouch, between 1-4 ounces in size,
keeping the valves of the stomach at the entry and
exit of food into the stomach which helps maintain
normal function.
There is no intestinal bypass performed, avoiding
many of the problems associated with malabsorption
of nutrients. In the past, the procedure was
usually reserved for high risk patients or super
obese patients with the intention of performing
another surgery at a later date. If necessary, the
second procedure would be either a duodenal switch
or gastric bypass.
Nowadays, no other surgeries are needed at all
anymore since patients loose as much as a gastric
bypass patient would. In general, all qualified
obese patients are considered and recommended for
undergoing this procedure. Most patients can lose
60 to 80% of their excess body weight over 6-12
months with sleeve gastrectomy alone.
Advantages of Vertical Sleeve Gastrectomy
Procedure
- Usually done laparoscopically
(minimally invasive) with robotic-assistance in
patients.
- Allows patients of any weight,
including the super super obese and high risk
patients, to undergo surgery with small
incisions
- Rapid weight loss
- Patients do not experience
diarrhea or significant ?Dumping Syndrome?
symptoms
- The portion of the stomach
producing hunger-stimulating hormones (Grehlin)
is removed
- The smaller stomach maintains
normal function with no rearrangement of the
intestines, reducing risks of protein and
vitamin deficiency and thus no significant
"Dumping Syndrome" symptoms
- Minimal patient effort to lose
and maintain weight loss
- Better weight loss than the
Adjustable Gastric Band procedures
- Safe in patients needing long
term aspirin, NSAID such as Motrin, Advil,
naprosyn, steroid use
Disadvantages of Vertical Sleeve Gastrectomy
Procedure
- Successful results depend on
willingness to adopt long-term lifestyle changes
- Weight loss may be slower than
more malabsorption procedure type like the
duodenal switch
Risks of Vertical Sleeve Gastrectomy Procedure
- Leakage
- Nausea/vomiting
- Acid reflux
- Weight regain
- Rarely, allows for second
surgery for more weight loss
- Gallstones

LAP-BANDŽ or REALIZE? Adjustable Gastric Band
This restrictive option has the least expected
weight loss of 40-55% of excess body weight.
Description of the LAP-BANDŽ System or REALIZE?
Adjustable Gastric Band
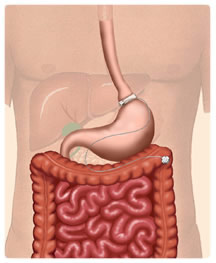 The
LAP-BANDŽ System or REALIZE? Adjustable Gastric
Band is placed laproscopically around the upper
part of the stomach. The band divides the stomach
into a small pouch above the band and larger pouch
below the band. The smaller pouch limits the
amount of food the patient can eat with the result
of fullness after eating a small amount of
food.
The
LAP-BANDŽ System or REALIZE? Adjustable Gastric
Band is placed laproscopically around the upper
part of the stomach. The band divides the stomach
into a small pouch above the band and larger pouch
below the band. The smaller pouch limits the
amount of food the patient can eat with the result
of fullness after eating a small amount of
food.
The opening of the stomach can be
increased or decreased by injecting or removing
saline from the band. Dr. Feng or his staff can
later control or adjust the amount of saline in
the band that is a unique feature of the Lap-BandŽ
or REALIZE? system and is a normal part of
follow-up post the procedure.
Dr. Feng no longer recommends
adjustable gastric band procedures due to the poor
weight loss compared with the sleeve gastrectomy,
gastric bypass or duodenal switch, in addition to
higher than expected incidence of severe
complications.
Advantages of LAP-BANDŽ System or REALIZE?
Adjustable Gastric Band Procedures
- Only procedure that can be
reversed if necessary
- Usually done laparoscopically
(minimally invasive)
- Easier to perform and
generally safer than other weight loss options
- Outpatient surgery
- Results in fewer nutritional
deficiencies
Disadvantages of LAP-BANDŽ System or REALIZE?
Adjustable Gastric Band Procedures
- Successful results depend on
the willingness to adopt long-term lifestyle
changes more than all the other surgeries, and
even the number of visits made after surgery
- Patients may have numerous
visits with Dr. Feng during the first year to
ensure proper band adjustment
- Requires the most effort from
the patient to lose and maintain weight loss
- Weight loss is usually slower
than the other surgeries and may take 2-3 years
to lose the predicted weight loss
- Weight loss is less than all
the other surgeries: sleeve gastrectomy, gastric
bypass, or duodenal switch
- Patients must avoid aspirin,
NSAIDs such as ibuprofen, Motrin, Advil,
naprosyn to avoid band erosion into the stomach
- Patients must always avoid
large meals to minimize risk of causing band
slippage or excessive esophagus stretching and
abnormal widening
Risks of LAP-BANDŽ System or REALIZE? Adjustable
Gastric Band Procedures
- Nausea/vomiting
- Food getting stuck, needing
deflation of band
- Overstretched, abnormally
widened esophagus
- Excessively tightened
- Infection
- Inadequate weight loss
- Weight regain
- Device malfunction
- Balloon, tube access port
breakage
- Access port flipping over
- Slippage of down along the
stomach causing vomiting
- Erosion of the silicone band
creating a hole in the stomach
- Gallstones

Combined Restrictive/Mal-absorption
Operations
Combined operations restrict the
amount of food intake and thus restricting
calories, but also limit absorption of certain
nutrients. These operations may also be more
effective in improving health problems related to
obesity compared with some restrictive-only
operations, but at higher risk of short and
long-term side effects and complications.

Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Procedure
This combined mostly restrictive and some
mal-absorption option, the Roux-en-Y Gastric
Bypass procedure, has an expected weight loss of
60-80% of excess weight, similar to the vertical
sleeve gastrectomy.
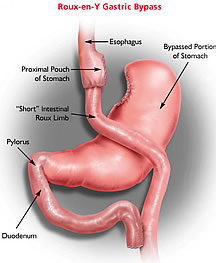 Description
of the Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass
Description
of the Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass
Second most common weight loss surgery performed
in the U.S. (less than half as much as sleeve
gastrectomy) and was previously considered the
gold standard of weight loss surgery.
Dr. Feng creates a small, upper stomach pouch
about 1-2 ounces in size, dividing it from the
lower stomach. This significantly restricts the
volume of food that can be eaten if solid protein
eaten first. This reduces the amount of calories
that can be eaten. He then divides the small
intestine to create a Y-shaped section to attach
to the stomach pouch. The lower stomach and a
portion of the small intestine is bypassed which
causes malabsorption of certain nutrients, with no
significant carbohydrate or fatty food
malabsorption. The procedure minimally limits the
nutrients the body can absorb because of the
bypass.
 Click
Here to watch an interactive video of the
Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Procedure
Click
Here to watch an interactive video of the
Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Procedure
Advantages of Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Procedure
- May be more effective in in
some studies in improving obesity-related health
problems than some restrictive procedures
- Rapid weight loss
- The portion of the stomach
producing hunger-stimulating hormones is
bypassed, and thus less hunger is experienced in
the first year after surgery but hunger usually
returns after about 9 months after surgery
- Better weight loss than the
Adjustable Gastric Band procedures
Disadvantages of Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass
Procedure
- Successful results depend on
the willingness to adopt long-term lifestyle
changes
- Patients may experience
long-term nutritional deficiencies, more so than
the restrictive procedures
- Decreased absorption of
calcium may bring on osteoporosis and related
bone diseases
- Decreased absorption of iron
and vitamin B12 may lead to anemia
- Weight loss may be slower than
more malabsorption procedure type like the
duodenal switch
- ?Dumping Syndrome? reaction
usually occurs when meals high in refined
sugars, carbohydrates, or rich fatty foods are
consumed
- Patients must avoid aspirin,
NSAIDs such as ibuprofen, Motrin, Advil,
naprosyn to avoid high risk of marginal ulcers
that can cause bleeding, perforation, abdominal
infection
- Possible risk of long-term
permanent severe hypoglycemia episodes from
nesidioblastosis, which may need high risk
reversal
Risks of Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Procedure
- Leakage
- Infection
- Vitamin and mineral
deficiencies
- Anemia
- Osteoporosis
- Strictures at the stomach
pouch connection to intestine
- Intestinal ulcers at margin of
connnection to stomach pouch
- Bowel Obstruction from
internal intestinal scars, internal hernias or
telescoping small intestine (intussusception)
- Dumping syndrome
- Gallstones
- Possible nesideoblastosis
disease causing severe hypoglycemia issues
- Combined operations are more
likely to lead to complications then restrictive
operations
- Weight regain

Duodenal Switch
This combined less restrictive and more
mal-absorption option, the Duodenal Switch, has an
expected weight loss of 70-90% of excess body
weight.
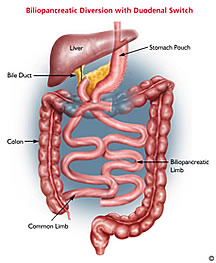 Description
of the Duodenal Switch
Description
of the Duodenal Switch
This procedure offers the ability
to eat larger portions foods than gastric bypass
or adjustable gastric banding, and even the
stand-alone vertical sleeve gastrectomy alone.
Weight loss can be long lasting. The patient may
experience more frequent and number of loose,
diarrheal bowel movements. Patients need to
closely monitor vitamin, protein and mineral
levels more than in any other surgery.
The stomach is reduced in size to
a long, tube-like vertical sleeve gastrectomy
pouch, 4-5 ounces in size with moderate
restriction of food intake. The sleeve gastrectomy
in the duodenal switich is considerably larger
than when done as a stand-alone procedure since
you have to eat more in the duodenal switch in
order to get enough nutrients into your body,
since the duodenal switch is so malabsoprtive,
even causing very smelly gas. Dr. Feng also
divides the small intestine to separate food from
the digestive juices, causing significant
malabsorption.
This surgery is best for patients
with BMI of 50 kg/m2 and above since sometimes too
much weight is lost, and thus dangerous to perform
in lighter, less morbidly obese patients.
Dr. Feng no longer recommends
this procedure since the weight loss is similar to
the sleeve gastrectomy (the way Dr. Feng does the
surgery) and the gastric bypass but with much
higher risk of complications and long term
concerns about excessive weight loss and
malnutrition.
 Click
Here to watch an interactive video of Duodenal
Switch Procedure
Click
Here to watch an interactive video of Duodenal
Switch Procedure
Advantages of Duodenal Switch Procedure
- Patients are able to consume
larger meals
- Rapid weight loss
- Stomach function remains
intact with normal stomach emptying, and thus
?Dumping Syndrome? seldom occurs, like the
sleeve gastrectomy
- The portion of the stomach
producing hunger-stimulating hormones is
removed, like the sleeve gastrectomy
- Better weight loss than the
Adjustable Gastric Band procedures
- Safe in patients needing long
term aspirin, NSAID such as Motrin, Advil,
naprosyn, steroid use
Disadvantages of Duodenal Switch Procedure
- Successful results depend on
the willingness to adopt long-term lifestyle
changes
- Some patients lose too much
weight
- May require lifetime use of
special foods and medications
- Higher risk of long-term
nutritional deficiencies due to more
malabsorption
- More invasive surgery
- Foul-smelling stools/gas after
surgery.
- Patients experience a higher
incidence of complications than any other
surgery
Risks of Duodenal Switch Procedure
- Excessive or too much weight
loss
- Leakage
- Infection
- Diarrhea
- Anemia
- Bowel obstruction
- Gallstones
- More vitamin and mineral
deficiencies
- Abdominal hernia
- Combined and more
malabsorptive operations are more likely to lead
to complications then restrictive operations
- Inadequate weight loss
- Weight regain
 Bariatric
surgery is a surgical procedure performed for
treatment of morbid obesity. The word "bariatric"
comes from the Greek: Baros which means
weight and Iatreia which means medical
treatment. Bariatric surgery has existed since the
1960's, having gone through significant evolution
from the early days of the jejunoileal or
jejunocolic bypass operations and the horizontal
gastroplasty or original "stomach stapling." Other
procedures that are no longer performed include
the silastic ring vertical gastroplasty and the
vertical banded gastroplasty. Modern day
procedures are usually performed by skilled
laparoscopic surgeons and include the Vertical
Sleeve Gastrectomy, the LAP-BANDŽ or REALIZE?
Adjustable Gastric Band procedures, the transected
Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass, and the Duodenal Switch.
Bariatric
surgery is a surgical procedure performed for
treatment of morbid obesity. The word "bariatric"
comes from the Greek: Baros which means
weight and Iatreia which means medical
treatment. Bariatric surgery has existed since the
1960's, having gone through significant evolution
from the early days of the jejunoileal or
jejunocolic bypass operations and the horizontal
gastroplasty or original "stomach stapling." Other
procedures that are no longer performed include
the silastic ring vertical gastroplasty and the
vertical banded gastroplasty. Modern day
procedures are usually performed by skilled
laparoscopic surgeons and include the Vertical
Sleeve Gastrectomy, the LAP-BANDŽ or REALIZE?
Adjustable Gastric Band procedures, the transected
Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass, and the Duodenal Switch. Most
common weight loss surgery performed in the U.S.
Most
common weight loss surgery performed in the U.S. The
LAP-BANDŽ System or REALIZE? Adjustable Gastric
Band is placed laproscopically around the upper
part of the stomach. The band divides the stomach
into a small pouch above the band and larger pouch
below the band. The smaller pouch limits the
amount of food the patient can eat with the result
of fullness after eating a small amount of
food.
The
LAP-BANDŽ System or REALIZE? Adjustable Gastric
Band is placed laproscopically around the upper
part of the stomach. The band divides the stomach
into a small pouch above the band and larger pouch
below the band. The smaller pouch limits the
amount of food the patient can eat with the result
of fullness after eating a small amount of
food. Description
of the Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass
Description
of the Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Description
of the Duodenal Switch
Description
of the Duodenal Switch