Duodenal Switch
Expected weight loss 70-90% of excess weight

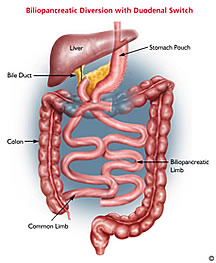
Description of Duodenal Switch
 This
procedure offers the ability to eat larger
portions foods than gastric bypass or adjustable
gastric banding and has reliable and long lasting
weight loss. You may experience more bowel
movements and need to closely monitor your
vitamin, protein and mineral levels.
This
procedure offers the ability to eat larger
portions foods than gastric bypass or adjustable
gastric banding and has reliable and long lasting
weight loss. You may experience more bowel
movements and need to closely monitor your
vitamin, protein and mineral levels.
The stomach is reduced in size to
a long, tube like vertical pouch, 4-5 ounces in
size with moderate restriction of food intake.
The small intestine is divided to separate food
from the digestive juices, causing significant
malabsorption. This surgery is best for patients
with BMI of 50 kg/m2 and above if
performed.
Dr. Feng no longer recommends
this procedure due to long term concerns about
side effects and complications. Fewer than 2% of
all patients in the world request or undergo this
procedure.
 Click
Here to watch an interactive video of Duodenal
Switch
Click
Here to watch an interactive video of Duodenal
Switch

Advantages of Duodenal Switch Procedure
- Patients are able to consume
larger meals
- Rapid weight loss
- Stomach function remains
intact with normal stomach emptying, and thus
“Dumping Syndrome” seldom occurs, like the
sleeve gastrectomy
- The portion of the stomach
producing hunger-stimulating hormones is
removed, like the sleeve gastrectomy
- Better weight loss than the
Adjustable Gastric Band procedures
- Safe in patients needing long
term aspirin, NSAID such as Motrin, Advil,
naprosyn, steroid use
Disadvantages of Duodenal Switch Procedure
- Some patients lose too much
weight
- May require lifetime use of
special foods and medications
- Higher risk of long-term
nutritional deficiencies due to more
malabsorption
- More invasive surgery
- Foul-smelling stools/gas after
surgery.
- Patients experience a higher
incidence of complications than any other
surgery
Risks of Duodenal Switch Procedure
- Excessive or too much weight
loss
- Leakage
- Infection
- Diarrhea
- Anemia
- Bowel obstruction
- Gallstones
- More vitamin and mineral
deficiencies
- Abdominal hernia
- Combined and more
malabsorptive operations are more likely to lead
to complications then restrictive operations
- Inadequate weight loss
- Weight regain
 This
procedure offers the ability to eat larger
portions foods than gastric bypass or adjustable
gastric banding and has reliable and long lasting
weight loss. You may experience more bowel
movements and need to closely monitor your
vitamin, protein and mineral levels.
This
procedure offers the ability to eat larger
portions foods than gastric bypass or adjustable
gastric banding and has reliable and long lasting
weight loss. You may experience more bowel
movements and need to closely monitor your
vitamin, protein and mineral levels.