|
|
Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Procedure
Expected weight loss 60-80% of excess
weight

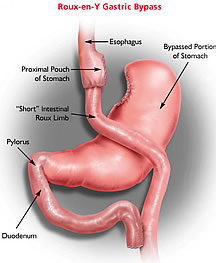 Description
of the Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Procedure Description
of the Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Procedure
Second most common weight loss surgery performed
in the U.S. (less than half as much as sleeve
gastrectomy) and was previously considered the
gold standard of weight loss surgery.
Dr. Feng creates a small, upper stomach pouch
about 1 ounce in size, dividing it from the lower
stomach. This significantly restricts the volume
of food that can be eaten if solid protein eaten
first. This reduces the amount of calories that
can be eaten. He then divides the small intestine
to create a Y-shaped section to attach to the
stomach pouch. The lower stomach and a portion
of the small intestine is bypassed which causes
malabsorption of certain nutrients, with no
significant carbohydrate or fatty food
malabsorption. The procedure minimally limits the
nutrients the body can absorb because of the
bypass.
 Click
Here to watch an interactive video of the
Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Procedure
Click
Here to watch an interactive video of the
Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Procedure

Advantages of Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Procedure
- May be more effective in in
some studies in improving obesity-related health
problems than some restrictive procedures
- Rapid weight loss
- The portion of the stomach
producing hunger-stimulating hormones is
bypassed, and thus less hunger is experienced in
the first year after surgery but hunger usually
returns after about 9 months after surgery
- Better weight loss than the
Adjustable Gastric Band procedures
Disadvantages of Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass
Procedure
- Successful results depend on
the willingness to adopt long-term lifestyle
changes
- Patients may experience
long-term nutritional deficiencies, more so than
the restrictive procedures
- Decreased absorption of
calcium may bring on osteoporosis and related
bone diseases
- Decreased absorption of iron
and vitamin B12 may lead to anemia
- Weight loss may be slower than
more malabsorption procedure type like the
duodenal switch
- “Dumping Syndrome” reaction
usually occurs when meals high in refined
sugars, carbohydrates, or rich fatty foods are
consumed
- Patients must avoid aspirin,
NSAIDs such as ibuprofen, Motrin, Advil,
naprosyn to avoid high risk of marginal ulcers
that can cause bleeding, perforation, abdominal
infection
- Possible risk of long-term
permanent severe hypoglycemia episodes from
nesidioblastosis, which may need high risk
reversal
Risks of Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Procedure
- Leakage
- Infection
- Vitamin and mineral
deficiencies
- Anemia
- Osteoporosis
- Strictures at the stomach
pouch connection to intestine
- Intestinal ulcers at margin of
connnection to stomach pouch
- Bowel Obstruction from
internal intestinal scars, internal hernias or
telescoping small intestine (intussusception)
- Dumping syndrome
- Gallstones
- Possible nesideoblastosis
disease causing severe hypoglycemia issues
- Combined operations are more
likely to lead to complications then restrictive
operations
- Weight regain
|
|
 Description
of the Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Procedure
Description
of the Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Procedure